Handball is a dynamic team discipline with precise mechanics, instant decisions and speed, where every second and step determines the outcome of an attack. Learning the structure of the game requires an understanding of specific movements, technical fundamentals and tactical flexibility. To know how to learn how to play handball, it is necessary to know the rules, master positional nuances and move from basic stance to competent combined attack.
History of handball: evolution from the field to the Olympics
To understand how to learn to play handball, it is important to know the origins of the discipline. The modern version of the format originated in northern Europe, where from the late 19th century, prototypes were actively developed with throwing, step restrictions and movement in a restricted area. Handball debuted at the Berlin Olympics in 1936 and by 1972 it had returned as a permanent discipline.
The game developed in two directions: a field version in stadiums and an indoor version, used in international competitions. The latter gained worldwide recognition and became the basis for all modern training programmes. Its evolution influenced everything from the shape of the goal to the players’ substitution protocols.
How to learn to play handball: learning the pitch structure and time rules
 Understanding the structure of the playing field and the time frame is essential for evaluating space and calculating attack times. In handball, the playing field is fixed: 40 metres long and 20 metres wide. The middle section is the goalkeeper’s area, a semi-circle with a radius of 6 metres, which attacking players are not allowed to cross with the ball.
Understanding the structure of the playing field and the time frame is essential for evaluating space and calculating attack times. In handball, the playing field is fixed: 40 metres long and 20 metres wide. The middle section is the goalkeeper’s area, a semi-circle with a radius of 6 metres, which attacking players are not allowed to cross with the ball.
A standard match consists of two halves of 30 minutes each, with a 10-minute break. In the event of a tie, two additional 5-minute halves are allowed in the playoffs. In the event of a tie, a series of 7-metre throws is taken. Time is calculated in seconds: from the selection of the moment of the pass to the exact completion of the attack. The referees stop the stopwatch at every off-ball, foul or technical break, making the match last 80-90 real minutes.
Fundamentals of technique: how do you learn to play handball correctly?
The fundamentals of technique are based on correct posture, balance and movement control. A beginner who wants to understand how to learn to play handball must first master the work of the lower limbs and shoulder girdle. The basic stance is as follows: feet shoulder-width apart, centre of gravity forward, knees slightly bent, arms apart for interceptions. This position provides agility when tackling and defending.
The rules restrict movement: only three steps are allowed without dribbling, followed by a pass, shot or hit to the ground. Moving the ball from the passive phase to the offensive phase requires training: changing feet, controlling breathing, receiving the ball at speed. Each movement forms a pattern, which is consolidated in practice.
Rules for ball possession and interaction: passing, dribbling and shooting.
Learning to play handball starts with understanding the technical actions. The rules strictly define what can and cannot be done. Dribbling is limited: one rebound cycle is allowed before picking up the ball, the second is considered a foul. The pass must be accurate, planned in advance, taking into account the position of the teammate and the defender.
The various shots, from the standard jump shot to the complicated backhand, require coordination, swing speed and control of hand position. To score successfully, the ball must travel more than 80 kilometres per hour. Experienced players reach up to 120 km/h. The position of the body, the moment of take-off from the ground and the choice of attack angle affect accuracy.
Typical mistakes made by beginners
The same mistakes are often made in handball in the early stages. The reasons are lack of understanding of the dynamics of the game, lack of visual analysis and poor reaction to changes in the opponent’s scheme. A mistake when entering the goalkeeper’s area, delaying the ball when changing attack, violating the number of steps are common blunders. Undisciplined players lose the team’s rhythm, disrupt combinations on the break and cause losses. Mistakes must be controlled and eliminated through visualisation and repetition of play.
Individual style and position specialisation
The development of a style of play follows the mastery of technique. Each player chooses a development path: playmaker, line player, fringe player. The central defender forms the attack, the linesman attacks in the area between the defenders and the full-backs play on the wings. Each style requires adaptation of shooting technique, stance and positioning. Analysing a player’s trajectory helps improve communication and reduce fouls. Statistics show that teams with clear roles make 28% fewer technical fouls.
Preparing for competition: practice and strategy
The formation of the competitive way of learning to play handball involves systematic training and participation in small tournaments. In this phase, it is especially important to learn: substitution protocol, rules of conduct for refereeing decisions, analysis of the opponent’s behaviour.
Role of strategy
Attacking tactics include blocking, feints and crosses. Defence is based on pass blocking and aggressive pressing. The formation adapts to the opponent’s behaviour. Teams using vertical pressing with many position changes win 72% of their games against static defences.
Training system
Professional dominance requires discipline and consistency. The question of how to learn to play handball in practice is solved by a comprehensive training programme: from technical basics to tactical tasks. Each training session should develop specific skills, not in a vague, but in a precise and measurable way.
The structure of the training cycle is divided into blocks: warm-up, technique, physics, tactics, match training. A successful programme is based on the following principle:
- Warm-up and joint mobilisation – up to 15 minutes (improving flexibility, reducing injuries).
- Technical block – up to 30 minutes (dribbling, passing, standing, shooting).
- Physical training – 20 minutes (reaction, acceleration, endurance).
- Tactical training – 15 minutes (movements without ball, interaction).
- Fighting – 20-30 minutes (simulation of match conditions).
This structure accelerates the development of game connections and minimises repeating mistakes.
Refereeing and basic infractions: how to avoid penalties and sanctions.
To learn to play handball, it is necessary to memorise a list of common fouls and understand what exactly is prohibited in all phases of the game. Not only participation, but also the rhythm of the team depends on following the rules.
Typical fouls in handball
- Exceeding the allowed number of steps without dribbling.
- Entering the goalkeeper’s area with the ball.
- Blocking a player without the ball with a tackle.
- Match violation: Crossing the area at an inappropriate moment.
- Hitting directly at the goalkeeper’s head on a throw from seven metres.
- Delay: Deliberately pausing to break rhythm.
How to learn to play handball: Conclusions
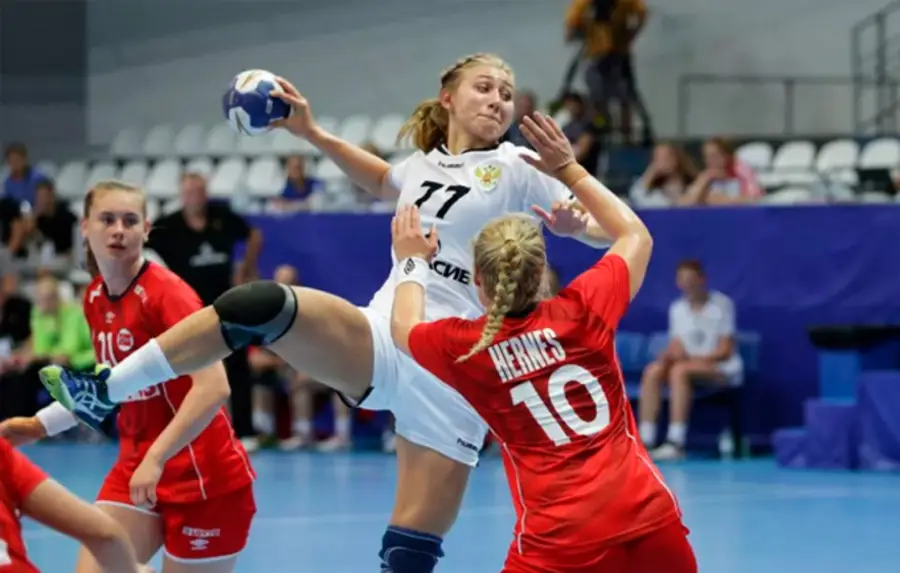 A complete understanding of how to learn to play handball consists of micro-details. Knowledge of the rules, technique, reaction, positional thinking, mental toughness, the ability to see the action area: each component reinforces the other. Handball requires calculation, but rewards those who act deliberately and systematically. Constant work on yourself, feedback, flexibility in decisions, adapting to the pitch, the break and the opponent are real tools that shape a player.
A complete understanding of how to learn to play handball consists of micro-details. Knowledge of the rules, technique, reaction, positional thinking, mental toughness, the ability to see the action area: each component reinforces the other. Handball requires calculation, but rewards those who act deliberately and systematically. Constant work on yourself, feedback, flexibility in decisions, adapting to the pitch, the break and the opponent are real tools that shape a player.
 en
en  ru
ru  de
de  ar
ar  es
es  nl
nl  hi
hi  fr
fr  it
it  pt
pt  el
el 









